Jun 7, 2017
Vitamin B-12 - A truly essential vitamin.
Webinar presented by: Celebrity Fitness Trainer Vinnie Tortorich & Andy Schreiber, CEO of Pure Vitamin Club
What is Vitamin B-12?
Also called “cobalamin,” Vitamin B-12 is one of the 8 members of the B vitamin family, and is considered one of the “essential vitamins.” The reason they’re called “essential” is that they are literally required for the human body to work properly. There are 13 essential vitamins:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D (D2 and D3)
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K (K1 & K 2)
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
- Vitamin B9 (Folate, or Folic Acid)
- Vitamin B12
The B Vitamins
- Water soluble (the body does not store them)
- Help the body convert food into fuel, which is used to produce energy
- Needed for healthy skin, hair, eyes, and liver
- Help the nervous system function properly
What Does Vitamin B-12 Do?
- Vitamin B12 helps keep the body’s nerve and blood cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all cells.
- Vitamin B12 also helps prevent a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia that makes people tired and weak.
How Is Vitamin B-12 Absorbed?
Two steps are required for the body to absorb vitamin B-12 from food.
- First, hydrochloric acid in the stomach separates vitamin B-12 from the protein to which vitamin B-12 is attached in food.
- After this, vitamin B-12 combines with a protein made by the stomach called intrinsic factor and is absorbed by the body.
- Some people have pernicious anemia, a condition where they cannot make intrinsic factor. As a result, they have trouble absorbing vitamin B-12 from all foods and dietary supplements.
How B-12 Works With Other B Vitamins
Vitamin B-12 works closely with Vitamin B-9 (Folate, or Folic Acid) to do the following:
- Make red blood cells and help iron work better in the body.
- Produce S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), a compound involved in immune function and mood
Vitamin B-12 works closely with Vitamin B-9 and Vitamin B-6 to do the following:
- Control blood levels of the amino acid homocysteine. High levels of homocysteine are associated with heart disease.
What Foods Contain Vitamin B-12?
Vitamin B-12 does not occur in any plant-based foods. The best dietary sources are:
- Meat
- Fish & Seafood
- Poultry
- Dairy Products
- Eggs
Some packaged foods, such as breakfast cereals, are “fortified” with Vitamin B-12, as well as with other vitamins, but these are by definition “processed” foods, and may not be the best choices for people trying to maintain a healthy diet.
Will Vitamin B-12 Give Me Energy?
- It’s a common myth that taking a Vitamin B-12 supplement will automatically give you a boost of energy.
- Unless you have a deficiency, or are in the “low normal” range of Vitamin B-12, there is no evidence that taking a B-12 supplement will increase your energy at all.
What Is A Vitamin B-12 Deficiency?
First it’s important to understand what constitutes a deficiency for Vitamin B-12. There is some question about where the actual clinical cutoff is. Plasma Vitamin B-12 levels are measured in pmol/L – picomoles per liter. Some important numbers to know:
- The currently accepted cutoff for clinical “deficiency” is 148 pmol/L.
- The “low normal” range is between 149 and 257 pmol/L
A major study from the 1970’s, the Framingham Offspring Study, revealed some very surprising data about
Vitamin B-12 levels in the population studied:
- Around 9% of the population fell below the clinical deficiency level (148 pmol/L)
- More than 16% of the population fell below 185 pmol/L, a seriously low level
- A full 39% of the population fell into the “low normal” range – below 258 pmol/L
According to a nutritional epidemiologist at Tufts University in Boston, many people who fall into the under 185 level are actually fully deficient, in terms of the health effects, and a significant percentage of people in the under 258, or “low normal” range, can exhibit some of the neurological symptoms of clinical deficiency.
What Are The Symptoms Of Vitamin B-12 Deficiency?
| • | Chronic Fatigue | • Mood Changes, Increased Depression or |
| • | Muscle Aches and Weakness | Anxiety |
| • | Joint Pain | • Abnormal Heart Problems / Palpitations |
| • | Difficulty Breathing/Shortness of Breath | • Poor Dental Health, Including Bleeding Gums |
| • | Feeling Dizzy | and Mouth Sores |
| • | Poor Memory | • Digestive Problems like Nausea, Diarrhea, or |
| • | Inability to Concentrate Well | Cramping |
| • | A Poor Appetite |
(A more serious deficiency can also cause pernicious anemia, which can cause memory loss, confusion, and even long-term dementia.)
Who Is Most At Risk For Vitamin B-12 Deficiency?
- People over 50
- People who take, or have taken for extended periods, antacids or proton inhibitors, such as Prilosec, Zantac, Prevacid, etc.
- People with digestive disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, IBS, celiac disease, etc.
- People who take the diabetes drug Metformin
- Vegans and vegetarians
- Women who take birth control pills
- Women with a history of infertility or miscarriage
What Do I Do If I Have A Vitamin B-12 Deficiency?
Research shows that for people who have a Vitamin B-12 deficiency, increasing dietary intake of meat, fish, dairy, etc., may not be enough, and supplementation may be necessary.
For most people with moderate deficiency, or who are in the “low normal” levels, oral supplementation is highly effective. For people with more serious deficiencies, it may be necessary to supplement with regular injections.
What Is The Best Form Of Vitamin B-12?
The two most common forms of Vitamin B-12 are methylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin.
Methylcobalamin is the form of B-12 that occurs in nature, and is by far the more preferred form for supplementation.
Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of B-12 that binds the actual B-12 to a cyanide molecule. It is used in many commercially available Vitamin B-12 supplements, and can even be found in many brands of injectable B -12 prescribed by physicians. In order to utilize Cyanocobalamin, the liver must actually dispose of the cyanide molecule, and convert the cobalamin back to the methyl form. This greatly diminishes the effectiveness, and taxes the liver.
So why do so many supplements, and even injections, use this form?
It’s CHEAPER!
A LOT CHEAPER!
Capsules, Liquid, or Tablet?
What delivery method for B-12 is the best?
- Because B-12 absorption is so easily affected by levels of stomach acid, any pills that are swallowed are not the best option.
- You will sometimes see “Soft Chews,” or other forms of candy used to deliver B-12, but these require sugar, or artificial sweeteners.
- Liquid supplements are effective, but difficult to transport and to dose accurately.
- Sub -lingual tablets dissolve under the tongue, delivering the B-12 directly to the blood stream, and are the most effective delivery method.
How Are Sub-Lingual Tablets Made?
- Vitamin B-12, as taken in supplements, is measured in “micrograms,” so the physical amount even in a high-dose supplement is very small.
- To visualize this – a typical multivitamin capsule contains about 850 mg of raw material. A high dosage of Vitamin B-12 is between 1,000 and 5,000 mcg, or between 1 and 5 mg.
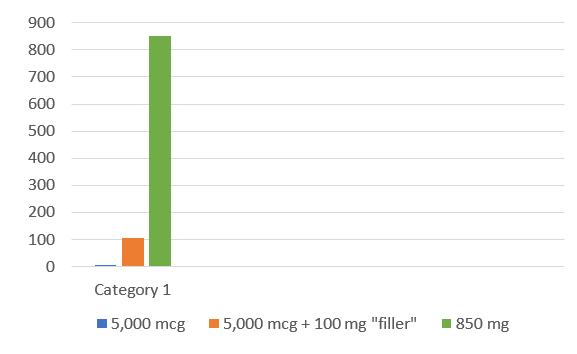 On the left, you can see that even
the highest dose of B-12, 5,000 mcg, barely even shows up against
the amount in a typical capsule.
On the left, you can see that even
the highest dose of B-12, 5,000 mcg, barely even shows up against
the amount in a typical capsule.
This means that a filler of some sort must be used to create a tablet large enough to even register or be able to handle.
So What Do Most Tablets Use As A Base?
Because the amount of cobalamin in a Vitamin B-12 supplement is so small, by definition it requires that the cobalamin be attached to some sort of base material. Virtually all products available use one of two such materials. Either:
- Lactose – a disaccharide sugar composed of galactose and glucose that is found in milk. Lactose makes up around 2 – 8% of milk.
- Lactose is a poor choice for a lot of people, as many people are lactose intolerant. Additionally, vegans, who need to rely on supplementation to meet their B-12 needs, cannot take lactose, as it is an animal product.
Sawdust
The other, and even more commonly used base material, or “bulking agent,” is Microcrystalline
Cellulose – a refined wood pulp used as a texturizer and anti-caking agent, and a bulking agent in food production.
Cellulose is the substance that makes up most of a plant’s cell walls, and is the most abundant organic compound on earth. Broccoli is essentially cellulose, as are strawberries, tomatoes, as well as wood.
NOT ALL CELLULOSE IS CREATED EQUAL
Microcrystalline Cellulose in particular is what is known as a “micro-nano particle,” meaning it is incredibly small.
According to George Burdock, PhD, and Sabine Teske, PhD,:
“Our cells cannot stop the micro-nano particles from entering them, and once there they are not able to be useful, but float in and out of the cell membranes, and basically clog up tiny places in our bodies, bioaccumulating as we take more, and causing background inflammation to rise.”
Great For The Floor Of A Honky-Tonk. Lousy For Your Body.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is one of the worst ingredients you can put in your body. Burdock and Teske state further:
“Once in the body, some particles have changed the shape or conformation of proteins, creating a protein similar to that produced in Alzheimer’s disease. Changing protein conformation can potentially create new allergenic proteins in organs to which the body could mount an immune response.”
Binders and Flow Agents
Both Lactose and Microcrystalline Cellulose need a binding agent in order to hold together as a tablet. Some of these ingredients, like “acacia gum,” or “guar gum,” are fairly benign. Others, such as certain sugars and synthetic polymers, are to be completely avoided.
While capsules can be made (thought most aren’t) without any form of lubricant, tablets are another matter. Without some sort of lubricant, the raw materials accumulate on the pins that punch out the tablets, making production impossible.
The lubricant, or “flow agent,” used by the vast majority of tablets is Magnesium Stearate, or Stearic Acid. Magnesium Stearate is not a source of magnesium and has no health benefits. It may, in fact, have a detrimental effect on your immune function, as stearic acid has been linked to suppression of T Cells, the main line of defense in your immune system. It also stimulates your gut to form a biofilm, which can prevent proper absorption of nutrients in your digestive tract.
Sweeteners, Artificial Flavors, and Artificial Colors
Because they’re meant to dissolve under the tongue, most sub-lingual tablets contain artificial sweeteners, such as sorbitol or mannitol, as well as artificial flavors and artificial colors.
For people who are taking vitamins in order to maintain their health, the use of these ingredients is highly counter-productive. As we say at Pure Vitamin Club – these are vitamins, not candy.
Pure Vitamin Club’s Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs
Pure Vitamin Club was founded in 2014, with a mission to provide the purest, highest quality nutritional supplements available, using the highest quality ingredients, in carefully balanced formulas, and absolutely no junk ingredients. We started with just one product – our Daily Multicap, an all-purpose multivitamin/multimineral formula.
In January 2016, we introduced our Broad Spectrum Magnesium Caps, a unique formulation of four different types of magnesium, specifically designed to provide the maximum benefit from each, while minimizing any unwanted side effects.
A Revolutionary Approach
PVC’s first two products were both capsules. While most manufacturers told us creating a capsule without fillers, flow agents, or other junk ingredients was impossible, we persisted, and by so doing, launched a revolution in nutritional supplementation.
Creating a tablet, however, was a much more difficult proposition. As laid out previously, we faced these challenges:
- Finding a base ingredient that was natural, non-toxic, could be tolerated well by everybody, and which would actually add nutritional benefit to the formula.
- Finding a way to hold the tablet together in the absence of any artificial binding agent.
- Finding a way to keep the integrity of the tablets while not impeding the production process.
- Creating a tablet that dissolved easily under the tongue, was an effective delivery system of the B-12, and was palatable.
If At First You Don’t Succeed…
After much research, a whole lot of trial and error, some more research, and a lot of dedication, we finally arrived at a formulation that delivered everything we wanted – the cleanest, most natural, and best sub-lingual Vitamin B-12 supplement ever created.
First Of Its Kind
- Methylcobalamin, the preferred form of B-12, in a dose of 2,000 mcg
- Calcium Citrate – a base ingredient that is also a nutrient.
- Calcium Laurate – a natural lubricant that does not inhibit absorption or hamper immune function. Made of calcium and lauric acid, a medium-chain triglyceride commonly found in coconut oil.
- No Magnesium Stearate!!
- No binders! The calcium citrate is compressible, so with just the right amount of pressure, the tablet holds together all on its own, yet still dissolves easily under the tongue.
- No artificial sweeteners. Remember, these are vitamins, not candy.
- No artificial flavors. Again – not candy.
- No artificial colors. We don’t care what color our vitamins are, as long as they’re pure and they work – and neither should you. So these are exactly the color the ingredients are.
How Do I Get It?
Currently, Pure Vitamin Products are available both on our website, www.purevitaminclub.com, as well as on Amazon and Ebay, as follows:
Website:
Daily Multicaps: 30-Day Plan (Subscription) or 90-Day Plan
Broad Spectrum Magnesium Caps: 90-Day Plan, or 90-Day Supply (Non-recurring order) Combo Pack (Multicaps + Magnesium): 90-Day Plan
On Amazon
Daily Multicaps: 90-Day Supply (Subscription or non-recurring)
Broad Spectrum Magnesium Caps: 90-Day Supply (Subscription or non-recurring) Combo Pack: 90-Day Supply (Subscription or non-recurring)
On Ebay
Daily Multicaps: 90-Day Supply
Broad Spectrum Magnesium Caps: 90-Day Supply
Combo Pack: 90-Day Supply
Options and Pricing
The New Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs will be available on www.purevitaminclub.com in the following ways:
Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs
Single Purchase – Non-Recurring
$19.95 + S/H
Combo Pack B
Daily Multicap + Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs
Delivered Every 90 Days
$37.95 + S/H
Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs
Subscription – Delivered Every 90 Days
$16.95 + S/H
Combo Pack C
Daily Multicap + Broad Spectrum Magnesium Caps + Sub-Lingual Vitamin B-12 Tabs
Delivered Every 90 Days
$54.95 + S/H
How To Modify Your Current Subscription
I want to add something to my current subscription and have the new item sent with my current items when my next regular shipment date comes up.
- Add the NEW item to the cart. Go to Check out.
- At Step 4, Select the option to ADD TO SUBSCRIPTION
- Complete the checkout process.
How To Modify Your Current Subscription
I want to remove everything in my current subscription and add a new item or items that will ship when my next regular shipment date comes up.
- Add the NEW item to the cart. Go to Check out.
- At Step 4, Select the option to REPLACE ITEMS IN SUBSCRIPTION
- Complete the checkout process.
How To Modify Your Current Subscription
I want to remove everything in my current subscription and add a new item or items that will ship immediately.
- Add the NEW item to the cart. Go to Check out.
- At Step 4, Select the option to REPLACE YOUR CURRENT SUBSCRIPTION
- Complete the checkout process.
How To Modify Your Current Subscription
I want to create an additional subscription that gets delivered to a different address that will ship immediately.
- Add the NEW items to the cart
- At Step 1, select "Ship to different address”
- At Step 2, use drop-down menu to select shipping address or enter new one
- At Step 4, select Credit Card and enter payment information
- Complete the checkout process That’s it.
Your Questions
Brent asks: “How much Vitamin B-12 is too much? What about the other Vit-B’s?”
Intake recommendations for vitamin B12 and other nutrients are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) developed by the Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) at the Institute of Medicine (IOM) of the National Academies. The “UL” is the “Tolerable Upper Limit” of any given nutrient.
There is no UL for Vitamin B-12. It is a water-soluble vitamin, and virtually impossible to overdose on. Any excess that the body cannot use will simply be excreted in the urine.
As for the other B Vitamins, most also have no recommended UL. The biggest exception is Vitamin B3, known as Niacin. Niacin is a vasodilator, and as such, in higher doses it can cause a reaction known as a “niacin flush” – a flushing of the skin, accompanied by a burning and itching sensation. While not dangerous, it can be very uncomfortable.
Lori asks: “Will increasing intake of Vitamin B-12 help lower cortisol levels?”
This is actually a sort of complicated answer. When cortisol is released in response to stress, inflammation occurs. High cortisol levels are associated with high homocysteine levels, a marker of inflammation. Vitamin B-12 helps control inflammation by converting homocysteine to methionine, an amino acid. The effects of high cortisol on inflammation can be buffered by vitamin B-12.
Paradoxically, B-12 can actually help for people whose cortisol levels are too low as well.
Bottom line is, B-12 helps to regulate levels of hormones, including cortisol, and helps to mitigate the inflammatory effects of elevated cortisol.
Manny asks: “Can B12 help older people with the elasticity of their skin?”
A number of vitamins contribute to maintaining healthy skin elasticity. These include Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and Vitamin E.
The B Vitamins, in particular B-12, folate, and B-6, help lower blood levels of the amino acid homocysteine. Elevated homocysteine can block enzymes that are essential for the normal meshing of collagen and elastin. Other B vitamins, including biotin and niacin, also contribute to healthy skin.
James asks: “Could you comment on the NIH fact sheet on B12? Is not folic acid needed in conjunction with B12?”
All of the B vitamins work well together on a number of fronts. However, overly high levels of folic acid, or folate, can mask the symptoms of B-12 deficiency by correcting the megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency without correcting the neurological damage that also occurs. That’s why we recommend a higher dose of B-12, but not the higher dose of Folate.
Adelina asks: “I don't get enough sleep, and as much as I try to prioritize it I just don't have time to go to bed earlier, or get up later. I'm pretty tired all the time. Would taking B-12 help me?
We got a number of variations of this question, including from Christine and others.
The answer is that B-12 will help only if the reason you’re tired is that you are either deficient in B -12, or in the “low normal” range. This can be determined by a simple blood test, but you can also try B-12 and see if it helps. A dose of at least 1,000 mcg or more would be necessary to correct the kind of deficiency or low level enough for you to really feel the difference.
Brett asks: “What time of day is it optimal to take B-12?”
Simple answer – it’s probably best to take B-12 in the morning, but there are no hard and fast rules.
Herbert asks: “Elite ultra runners that are VEGAN living/training/racing at altitude: how many strikes against them if not taking B-12 sublingual?”
Simple answer – three strikes! Vegans NEED B-12 supplementation, and ultra athletes will also benefit greatly from increased supplementation.
Debra asks: “Vinnie, I have chosen to take a sublingual B12 and read that methylcobalamin is what you want...not cyanocobalamin. So I switched. I take 5000 per day once in the a.m. How's that? Also I'm old. 62. But still kinda cute.”
It’s great that you’re taking methylcobalamin, instead of cyanocobalamin, and also great that you’re taking a sublingual. 5,000 mcg in the morning is a great dose, though you may be just fine on a lower dose, like our 2,000 mcg formula.
The biggest issue is what those sub-lingual tablets are made of, and what additional crap ingredients they contain. Whatever you’re taking – read the label! If you see Magnesium Stearate, Stearic Acid, Mannitol, Sorbitol, etc. – throw them out.

